Find further information on the Conservation of Freshwater Ecosystem Values (CFEV) Program and its data at www.dpipwe.tas.gov.au/cfev.
TitleRiparian vegetation condition (natural and/or exotic)
CustodianWater and Marine Resources Division, Department of Primary Industries, Parks, Water and Environment
CreatorGIS Unit, Information and Land Services Division, Department of Primary Industries and Water
DescriptionProportion of native and/or exotic vegetation present within the riparian zone of saltmarshes, rivers, waterbodies and wetlands
Input data
Lineage
A data layer presenting the proportions of natural* and exotic* vegetation within the riparian zone was developed by intersecting the CFEV modified TASVEG spatial data layer with the CFEV buffer zone spatial data layer. For rivers, the buffer zone is a 50 m strip either side of the river section, and for saltmarshes, waterbodies and wetlands it is 100 m around the spatial unit.
The percentage area of natural vegetation present within the buffer area was calculated and assigned to the data as a score ranging between 1 (100% native vegetation present or near-natural to natural condition) and 0 (0% native vegetation present or degraded condition).
The same method was used for identifying the extent of exotic (also termed ‘cultural’) vegetation within waterbody riparian zones. The exotic riparian vegetation score also ranges between 1 (0% exotic vegetation present or near-natural to natural condition) and 0 (100% exotic vegetation present or degraded condition).
A riparian vegetation score was then assigned to river sections, waterbodies and wetlands as outlined below. The saltmarsh riparian vegetation spatial data was visually inspected in combination with aerial photographs (for assessing the lateral extent and width of backing vegetation, rather than directly assigned to individual spatial units.
* The natural class included natural non-vegetation TASVEG codes, such as water, rocks, etc. and the exotic (cultural) class included unnatural non-vegetation codes such as built-up areas.
Data limitations
As per the Tasmanian Vegetation Map (TASVEG) data set.
Date createdSeptember 2004
Scale and coverage1:25 000; Statewide
References
DPIW. (2003). TASVEG 0.1 May 2003. Tasmanian Monitoring and Mapping Program. Department of Primary Industries and Water, Hobart.
Harris, S. and Kitchener, A. (2003) Tasmania's vegetation: a technical manual for TASVEG, Tasmania's vegetation map: Version 1.0. (Draft). Department of Primary Industries, Water and Environment, Hobart.
TitleRiparian vegetation condition (natural and/or exotic)
Column headingRS_NRIPV (Native riparian vegetation – local), RS_ACNRIPV (Native riparian vegetation – accumulated upstream), RS_WB_CRIVE (Exotic riparian vegetation), WB_NRIVE (Native riparian vegetation), WL_NRIVE (Native riparian vegetation)
Input data
Type of dataContinuous but also exists in a categorical format (see Table 1).
Number of classesRS_NRIPV = 4, RS_ACNRIPV = 4; WB_CRIVE = 4, WB_NRIVE = 4, WL_NRIVE = 4
Assigning values to ecosystem spatial units
Rivers section native riparian vegetation for the local river section catchment area (RS_NRIPV)
River section native riparian vegetation accumulated for all upstream river section catchment areas (RS_ACNRIPV)
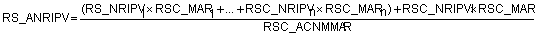
Where:
RS_ACNRIPV = Accumulated native riparian vegetation score for the river section
RS_NRIPV (1…n) = Native riparian vegetation score of the upstream river sections
RSC_MAR (1…n) = Current MAR value of the upstream RSCs
RS_NRIPV = Native riparian vegetation score of the local river section
RSC_MAR = Current MAR value of the local RSC
RSC_AMARNM = Accumulated current MAR value for the RSC (includes the MAR of the local RSC)
Note: In this accumulation, the boundaries of the upper catchment stopped where a RSC was directly downstream of a waterbody or a wetland of area >1 ha. This allowed for the influence of a waterbody/wetland acting as a sink for catchment-derived sedimentation. A diagram illustrating this process is presented in Figure 1.
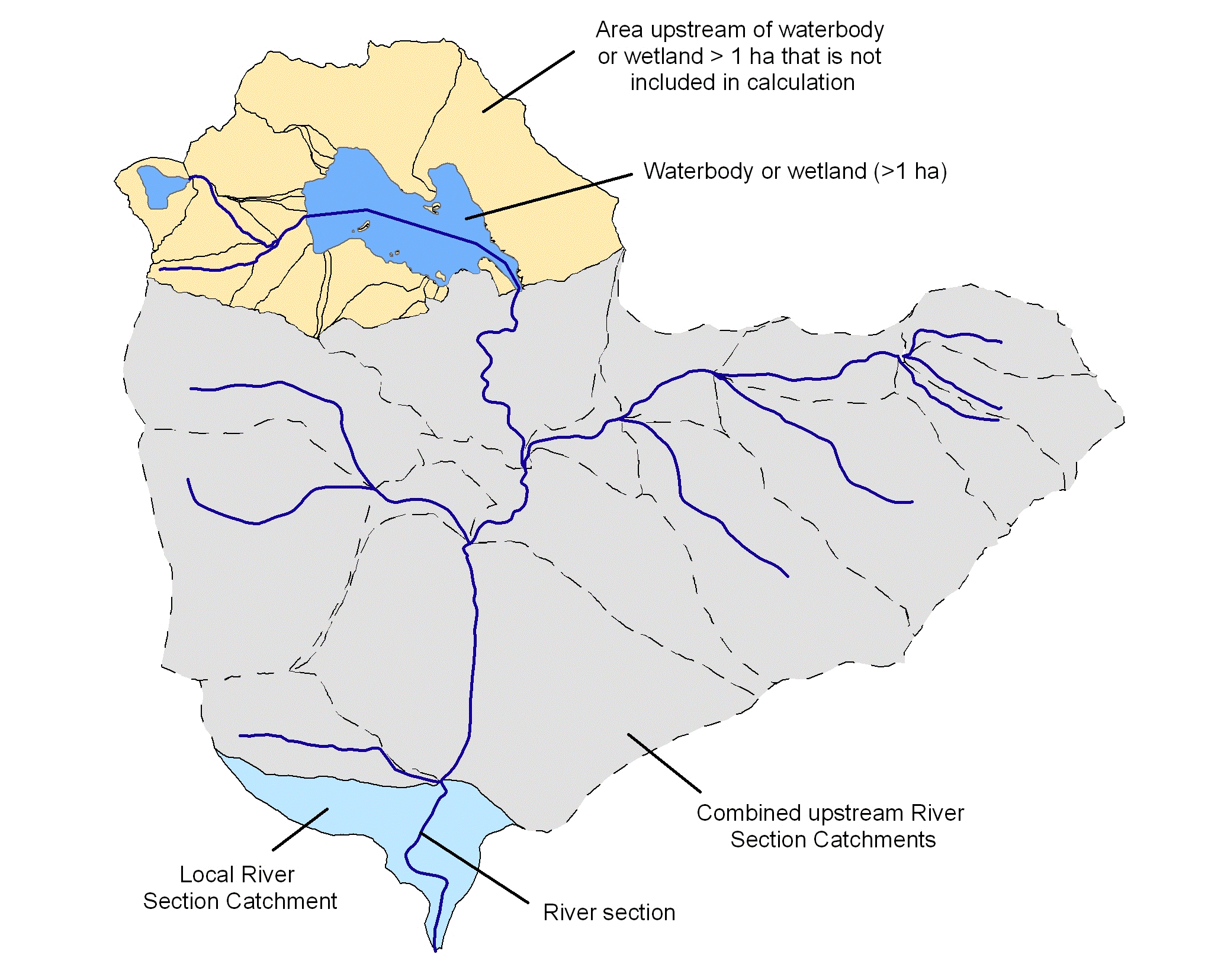
Figure 1. Illustration of catchments showing the local and upstream RSCs contributing to the calculation of the accumulated native riparian vegetation scores. Dotted lines show RSC boundaries.
Waterbodies (WB_NRIVE) and wetlands (WL_NRIVE) native riparian vegetation
Waterbodies exotic riparian vegetation (WB_CRIVE)
Each of the river, waterbody and wetland spatial data layers had the continuous riparian vegetation condition data categorised according to Table 1. The categorical data was used for reporting and mapping purposes.
Table 1. Riparian vegetation condition categories for rivers, waterbodies and wetlands.
Category | Rivers (Native) (local and accumulated) (Min to max values) | Waterbodies (Exotic) (Min to max values) | Waterbodies (Native) (Min to max values) | Wetlands (Native) (Min to max values) |
1 | 0 | 0 to <0.2 | 0 | 0 |
2 | >0 to 0.2 | 0.2 to <0.8 | >0 to 0.2 | >0 to 0.2 |
3 | >0.2 to 0.8 | 0.8 to <1 | >0.2 to 0.8 | >0.2 to 0.8 |
4 | >0.8 to 1 | 1 | >0.8 to 1 | >0.8 to 1 |
CFEV assessment framework hierarchy